Pointers in C language is a powerful tool that enables us to work with memory addresses and access data indirectly. Pointers play a vital role in C programming, allowing us to manipulate memory, create dynamic data structures, and optimize code efficiency. In this content, we will delve into the concept of pointers in C language and explore their significance in programming.
In C or other programming languages, there is the concept of variables. These variables are used to hold the value. You can use these variables during programming. However, few tasks do not require variables, but they do require the addresses of those variables. The address of the variables means the real memory location where these variables reside. In this topic, you will learn about C pointers. Pointers can be defined as the type of variable that contains the addresses of other variables that can have some value.
Declaring a Pointer:
Like variables, C programming pointers must be declared before they can be used programmatically. Pointers can be named as long as they follow the C naming convention.
Syntax:
data_type * pointer_variable_name;
Where,
- data_type is the base type of a C variable type pointer and indicates the type of variable pointed to by the pointer.
- The indirect operator asterisk (*: the same asterisk used for multiplication) declares a pointer.
Initialize a pointer:
After declaring the pointer, initialize it as a standard variable with a variable address. If the C programming pointer is not initialized and not used in the program, the results are unpredictable and can be disastrous.
To get the address of a variable, use the ampersand (&) operator that precedes the name of the variable whose address is required.
Syntax:
pointer = &variable;
For example:
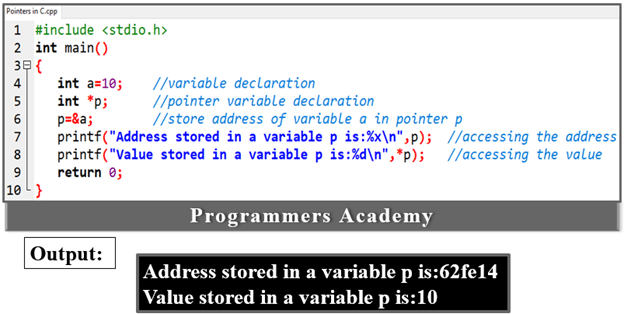
Here Code:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a=10; //variable declaration
int *p; //pointer variable declaration
p=&a; //store address of variable a in pointer p
printf("Address stored in a variable p is:%x\n",p); //accessing the address
printf("Value stored in a variable p is:%d\n",*p); //accessing the value
return 0;
}
Types of Pointers in C Language:
There are different types of C pointers. The basic types of pointers that are commonly used are:
1. Null Pointer: A null pointer is a pointer that does not point to anything. Generally, refers to the base address of the segment. If nothing is assigned to the pointer, it will be a null value.
For example:
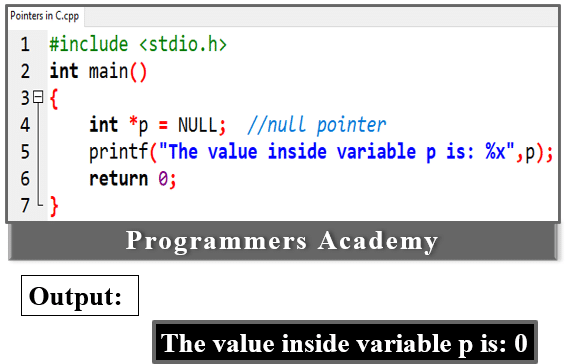
Here Code:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int *p = NULL; //null pointer
printf("The value inside variable p is: %x",p);
return 0;
}
2. Wild Pointer: Uninitialized pointers are called wild pointers. This type of pointer is initialized at run time when it needs to be used. This type of pointer is called a wild pointer.
For example:
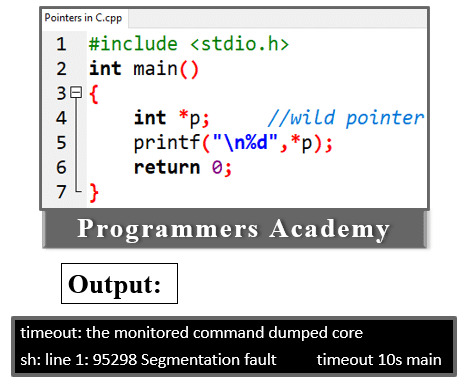
Here Code:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int *p; //wild pointer
printf("\n%d",*p);
return 0;
}
3. Void Pointer: In C programming, empty pointers are also known as generic pointers. There is no standard data type. The void pointer is created using the void keyword. It can be used to store the address of any variable.
For example:
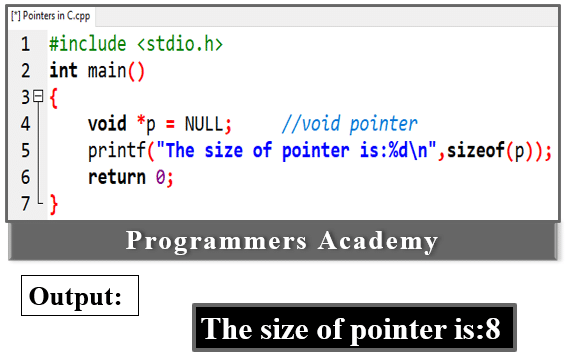
Here Code:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
void *p = NULL; //void pointer
printf("The size of pointer is:%d\n",sizeof(p));
return 0;
}
4. Dangler Pointer: This type of pointer can be created by deleting the object without changing the value of the pointer.
5. Generic Pointer: This type of pointer is declared by a variable of type void. It is called a generic pointer because it is a null data type. These types of pointers do not point to data.
Advantages of Pointers in C Language:
- Pointers help you access memory locations.
- Pointers provide an efficient way to access the elements of an array structure.
- Pointers are used for dynamic memory allocation and deallocation.
- Pointers are used to form complex data structures, such as linked lists, charts, and trees.
Disadvantages of Pointers in C Language:
- Pointers are a bit tricky to understand.
- Pointers can cause various errors, such as segfaults, or accessing memory locations that you don’t need at all.
- Specifying an incorrect value for the pointer can corrupt memory.
- Pointers can also cause memory leaks.
- Pointers are relatively slower than variable pointers.
- Programmers find it very difficult to manipulate pointers. Therefore, it is the responsibility of the programmer to handle the pointer with care.
Conclusion:
Pointers are nothing more than memory locations where data is stored. Pointers are used to access memory locations. There are different types of pointers, such as null pointers, wild pointers, empty pointers, and other types of pointers. You can use pointers with arrays and strings to access items efficiently. You can create a function pointer to call a function dynamically. Arithmetic operations can be performed on pointers, known as pointer arithmetic. A pointer can also point to a function that makes it easy to call multiple functions by defining an array of pointers. You can use the boxed empty pointer when working with different types of variable data.
Learn All About Efficient File Dealing in C
FAQ
What is a pointer in the C language?
A: A pointer in the C language is a variable that stores the memory address of another variable. It allows indirect access to the data stored at that memory location.
How are pointers useful in C programming?
A: Pointers are powerful tools in C programming as they enable dynamic memory allocation, facilitate passing parameters by reference, and allow efficient manipulation of data structures such as arrays and linked lists.
How do pointers work?
A: Pointers store the memory address of variables. By dereferencing a pointer, we can access the value stored at that memory location. Pointers can be used to manipulate data directly in memory, providing flexibility and efficiency in C programming.
Can pointers be used for memory management?
A: Yes, pointers are essential for memory management in C. They allow dynamic allocation and deallocation of memory, providing control over the lifetime and usage of memory resources.
Are pointers difficult to use?
A: Pointers can be challenging to understand and use correctly. They require a good understanding of memory concepts and careful handling to avoid common pitfalls such as memory leaks and segmentation faults. However, mastering pointers is crucial for efficient C programming.
References:
- https://fresh2refresh.com/c-programming/c-pointer/#:~:text=Pointers%20in%20C%20language%20is,char%2C%20double%2C%20short%20etc.
- https://www.programiz.com/c-programming/c-pointers
- https://www.tutorialspoint.com/cprogramming/c_pointers.htm
- https://www.guru99.com/c-pointers.html
- https://beginnersbook.com/2014/01/c-pointers/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pointer_(computer_programming)

