Variable in C play an important role. It can also be said that variables are the backbone of many programming languages. Variables in C are used to store data in various formats. It stores all the data and acts as a memory card to use while the program is running. Different types of variables require different amounts of memory and there is a specific set of operations that can be applied to them.
Rules for Defining Variables in C:
- C variables must not start with a number. Otherwise, the variable will not be valid. For example (a string is not a valid variable).
- Blank spaces are not allowed between variables. For example (string 1 is not valid, string_one is a valid variable).
- Keywords cannot be defined as variables. For example (para is not a valid variable as it is used as a keyword in C).
- C is a case-sensitive language, so use of upper and lower case is considered a different variable. For example (NUMBER and number are treated as two different variables in C).
- Variable names can be a combination of strings, numbers, and special characters such as underscores (_).
Variable Declaration in C Language:
A typical variable declaration has the form:
data_type variable_name;
where,
data_type: Indicates the type of data to be stored. Data types include int, float, char, double, longint, and so on.
variable_name: Indicates the name of the variable. It can be anything other than keywords.
For example:
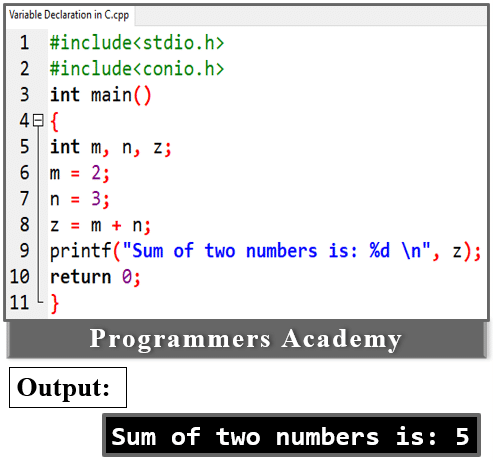
Here Code:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
int main()
{
int m, n;
m = 2;
n = 3;
z = m + n;
printf("Sum of two numbers is: %d \n", z);
return 0;
}
Initialize variables C Language:
Initializing a variable in C means assigning a value directly to the variable as it is declared. The syntax is:
data_type variable_name = value;
For example:
int a = 10;
The variable “a” is created and initialized with a value of 10.
More about this source text
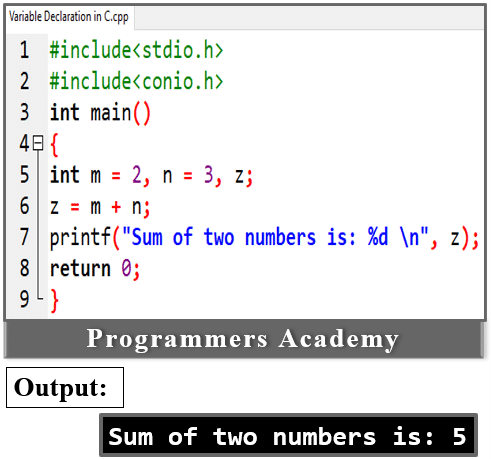
Here Code:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
int main()
{
int m = 2, n = 3;
z = m + n;
printf("Sum of two numbers is: %d \n", z);
return 0;
}
Types of Variable in C Language:
There are five types of variables declaration in C Language:
1. Local Variables:
local functions can change the value of a variable and used within a function are called local variable and also must be declared only before they can be used.
Example:
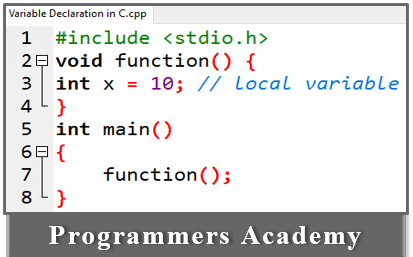
Here Code:
#include <stdio.h>
void function() {
int x = 10; // local variable
}
int main()
{
function();
}
In the above code, x can only be used within the scope of function (). An error will occur if it is used in the main function.
2. Global Variables:
Variables declared outside of the function are called global variables. Any function can change the value of a variable.
Example:
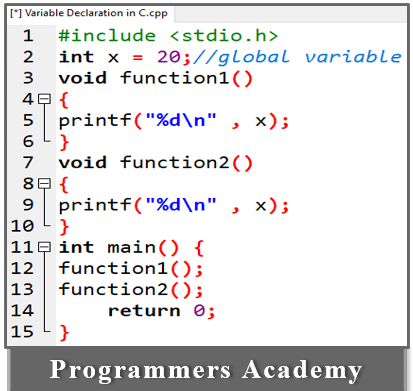
Here Code:
#include <stdio.h>
int x = 20;//global variable
void function1()
{
printf("%d\n" , x);
}
void function2()
{
printf("%d\n" , x);
}
int main() {
function1();
function2();
return 0;
}
In the above code, all functions can access the global variable, so both functions can use the global variable x.
3. Static variables:
Variables declared with the static keyword are called static variables.
Example:
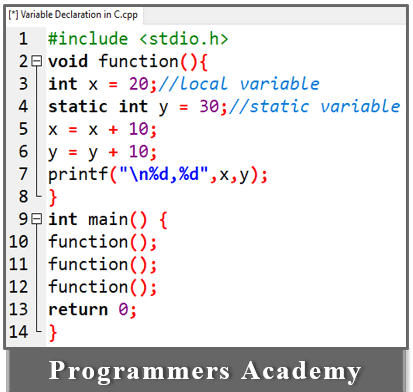
Here Code:
#include <stdio.h>
void function(){
int x = 20;//local variable
static int y = 30;//static variable
x = x + 10;
y = y + 10;
printf("\n%d,%d",x,y);
}
int main() {
function();
function();
function();
return 0;
}
In the example above, local variables always print the same value each time a function is called, while static variables print incremental values on each function call.
4. Automatic variables in C:
All variables declared within a function are considered automatic variables by default.
Example:

Here Code:
#include <stdio.h>
void function()
{
int x=10;//local variable (also automatic)
auto int y=20;//automatic variable
}
int main() {
function();
return 0;
}
In the example above, both x and y are automatic variables. The only difference is that the variable y is explicitly declared with the auto keyword.
5. External variables:
External variables are declared using the extern keyword. ‘extern’ keyword can be used in C language.
Example:
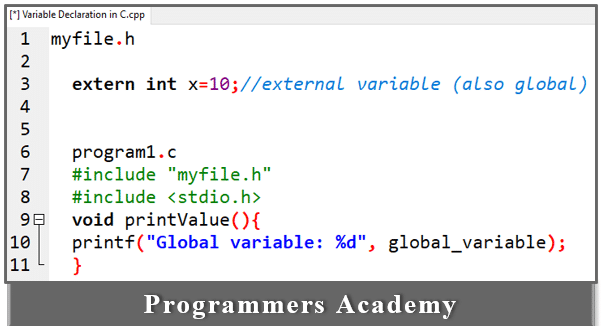
Here Code:
myfile.h
extern int x=10;//external variable (also global)
program1.c
#include "myfile.h"
#include <stdio.h>
void printValue(){
printf("Global variable: %d", global_variable);
}
In the example above, x is an external variable used by multiple files.
Conclusion:
In this article, you have learned how to implement them using declarations, initializations, syntax, and programs. We have also discussed the types of variables in C and the rules for defining them.
Read More For Master The String in C Language

